biology: The study of living things. The scientists who study them are known as biologists.
biomedical: Having to do with medicine and how it interacts with cells or tissues.
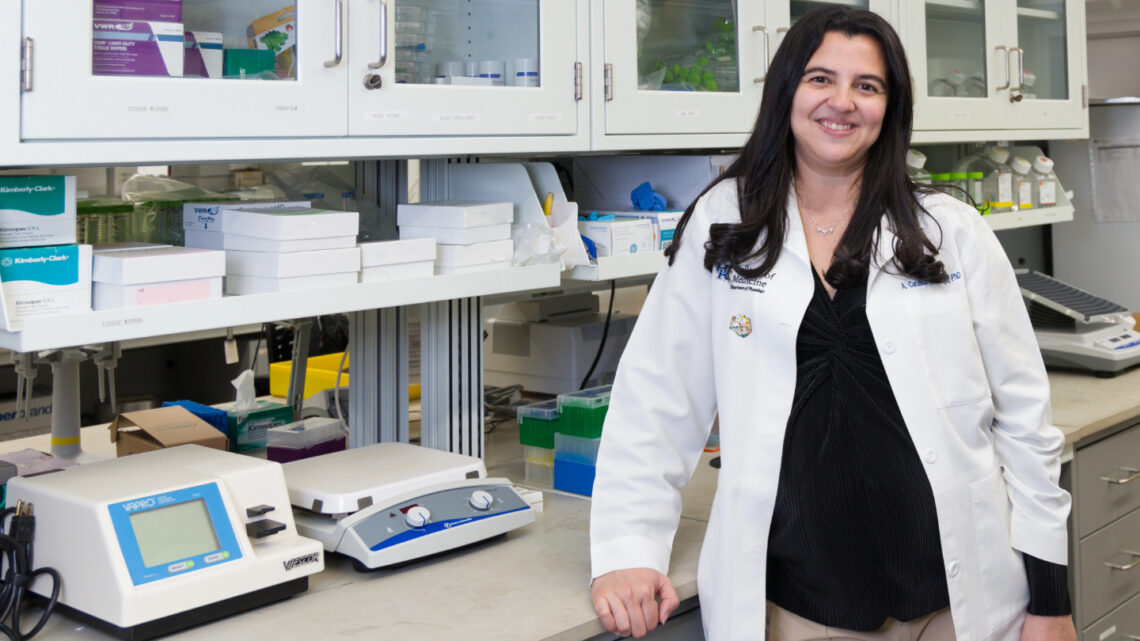
biomedical engineer: An expert who uses science and math to find solutions to problems in biology and medicine; for example, they might create medical devices such as artificial knees.
biomedical engineering: Combining engineering and biology to aid human health. Professions in this field develop artificial limbs, use biotechnology to produce new drugs and develop models to understand how diseases work.
blood vessel: A tubular structure that carries blood through the tissues and organs.
cell: (in biology) The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Typically too small to see with the unaided eye, it consists of a watery fluid surrounded by a membrane or wall. Depending on their size, animals are made of anywhere from thousands to trillions of cells. Most organisms, such as yeasts, molds, bacteria and some algae, are composed of only one cell.
code: (in computing) To use special language to write or revise a program that makes a computer do something. (n.) Code also refers to each of the particular parts of that programming that instructs a computer’s operations.
coding: (in computing) A slang term for developing computer programming — or software — that performs a particular, desired computational task.
cyst: A group of cells that form a type of bubble-like shell or sac. Some cysts develop as a result of disease or tissue damage. Others may develop as a normal, protective feature during certain phases of a parasite’s maturation.
electronics: Devices that are powered by electricity but whose properties are controlled by the semiconductors or other circuitry that channel or gate the movement of electric charges.
engineering: The field of research that uses math and science to solve practical problems. Someone…
Read the full article here