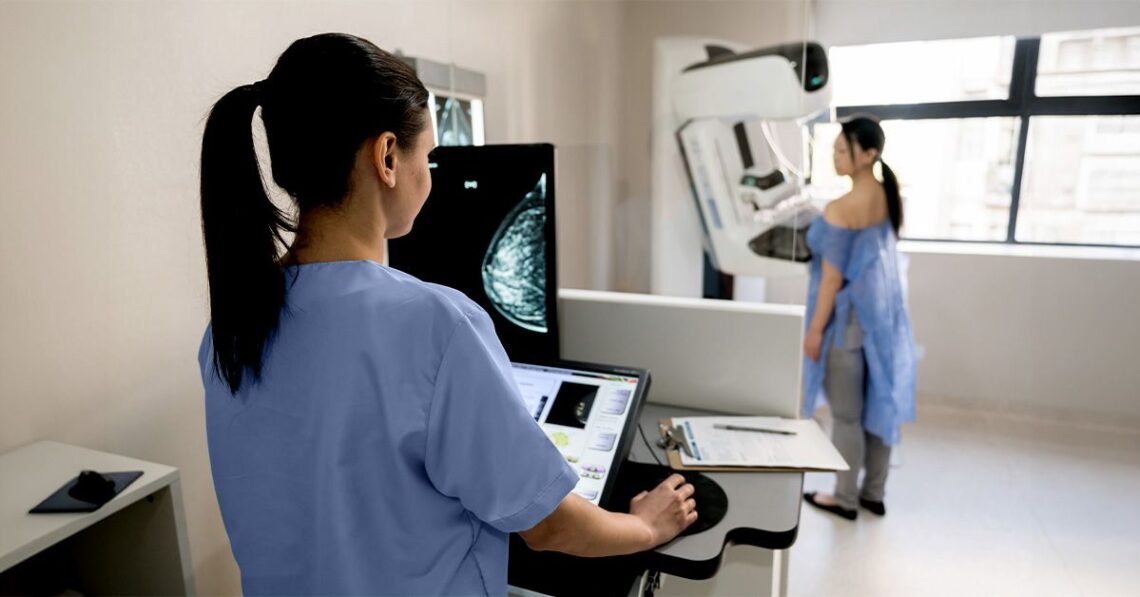
- New breast cancer screening guidelines suggest women at an average risk should begin mammograms at age 40 as opposed to the previous recommendation of age 50.
- Officials at the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force say the earlier screenings should save 20% more lives.
- They add that people with a history of breast cancer or other factors that increase their risk should speak with their doctor for individualized recommendations.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has issued new guidelines for breast cancer screening in which they recommend that women between the ages of 40 and 74 receive a mammogram every two years.
Previous guidelines from 2016 suggested that screening should begin at 50. Task force members said they did not see the need for routine screening in women over the age of 74.
The researchers at the USPSTF said they have completed a comprehensive
They said that this thorough review led them to conclude that the evidence comparing the effectiveness of various breast cancer screening strategies is inconclusive, underlining the complexity of this issue.
In 2016, the task force recommended screening, most commonly mammograms, as most effective when completed every two years starting at age 50 and continuing until age 74. The scientists said people under 50 should undergo screening based on their risk. They did not find that screening past 74 reduced breast cancer mortality.
The current recommendations change the starting age to 40 rather than 50. The task force says this change has the potential to save 20% more lives than the previous guidelines.
According to the task force, this recommendation applies to cisgender women and all other people assigned female at birth. It includes women at average risk of breast cancer as well as those with a family history of breast cancer and those with dense breasts.
It does not apply to:
- People with a history of breast cancer
- Those at high…
Read the full article here