anatomy: (adj. anatomical) The study of the organs and tissues of animals. Or the characterization of the body or parts of the body on the basis of structure and tissues. Scientists who work in this field are known as anatomists.
ancestor: A predecessor. It could be a family forebear, such as a parent, grandparent or great-great-great grandparent. Or it could be a species, genus, family or other order of organisms from which some later one evolved. For instance, ancient dinosaurs are the ancestors of today’s birds. (antonym: descendant)
anthropologist: A social scientist who studies humankind, often by focusing on its societies and cultures.
argon: An element first discovered on August 13, 1894, by Scottish chemist Sir William Ramsay and English physicist John William Strutt, better known as Lord Rayleigh. Argon was the first “noble” gas, meaning one that does not react chemically with other elements. For its discovery, Ramsey would receive the 1904 Nobel Prize in chemistry and Rayleigh the 1904 Nobel Prize in Physics.
ash: (in geology) Small, lightweight fragments of rock and glass spewed by volcanic eruptions. (in biology) A group of deciduous trees in the olive family that are popular in landscaping and for timber.
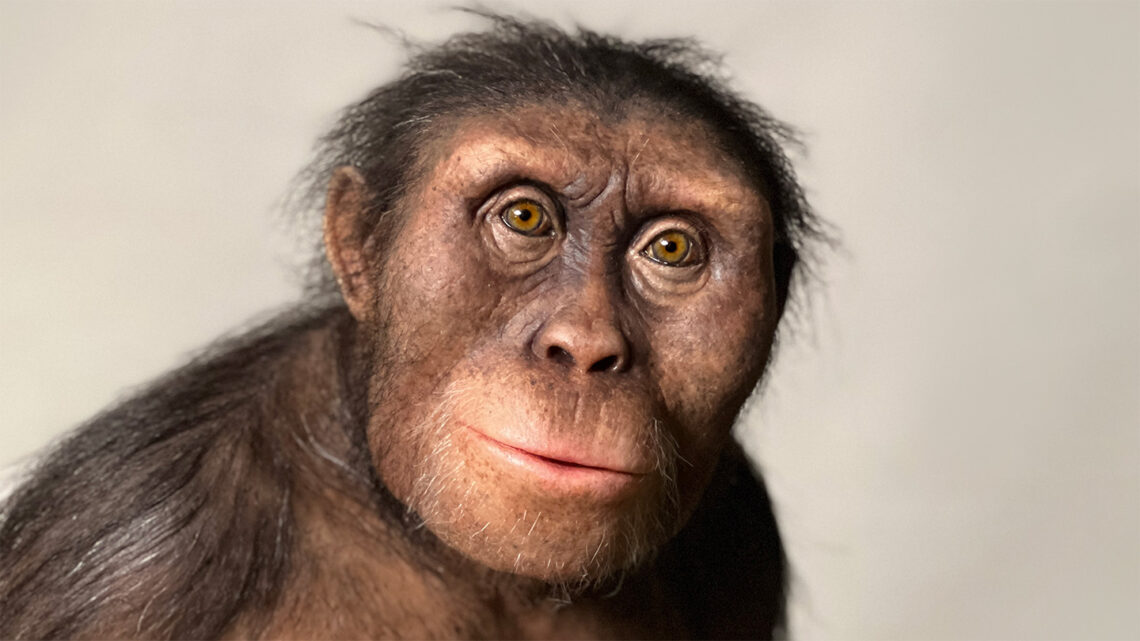
Australopithecus: An extinct genus of hominids that lived in East Africa from about 4 million to 2 million years ago. Members of this genus were known as australopithecines.
colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
decay: (for radioactive materials) The process whereby a radioactive isotope — which means a physically unstable form of some element — sheds energy and subatomic particles. In time, this shedding will transform the unstable element into a slightly different but stable element. For instance, uranium-238 (which is a radioactive, or unstable, isotope) decays to radium-222 (also a radioactive isotope), which decays to radon-222 (also radioactive), which decays to polonium-210…
Read the full article here