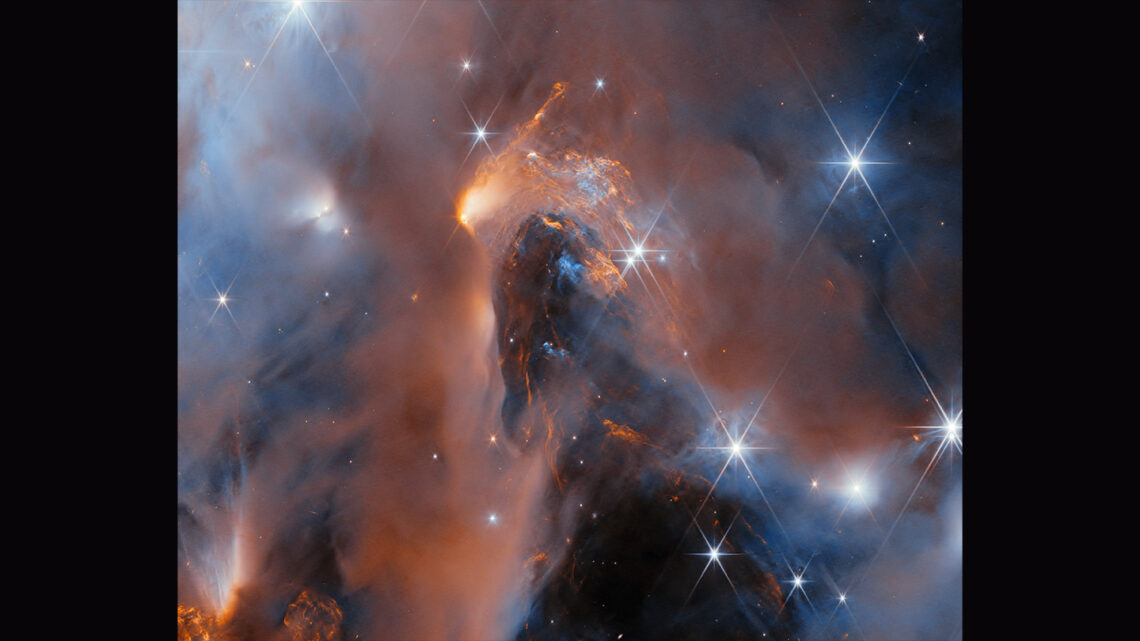
astronomer: A scientist who works in the field of research that deals with celestial objects, space and the physical universe.
astrophysicist: A scientist who works in an area of astronomy that deals with understanding the physical nature of stars and other objects in space.
brown dwarf: A would-be star that never became massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion.
celestial object: Any naturally formed objects of substantial size in space. Examples include comets, asteroids, planets, moons, stars and galaxies.
chemical: A substance formed from two or more atoms that unite (bond) in a fixed proportion and structure. For example, water is a chemical made when two hydrogen atoms bond to one oxygen atom. Its chemical formula is H2O. Chemical also can be an adjective to describe properties of materials that are the result of various reactions between different compounds.
cloud: A plume of molecules or particles, such as water droplets, that move under the action of an outside force, such as wind, radiation or water currents.
colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
constellation: Patterns formed by prominent stars that appear to lie close to each other in the night sky. Modern astronomers divide the sky into 88 constellations, 12 of which (known as the zodiac) lie along the sun’s path through the sky over the course of a year. Cancri, the original Greek name for the constellation Cancer, is one of those 12 zodiac constellations.
disk: A round, flat and usually fairly thin object. (in astronomy) A rotating cloudlike collection of gases, dust or both from which planets may form. Or the structure of certain large rotating bodies in the cosmos, including spiral galaxies.
environment: The sum of all of the things that exist around some organism or the process and the condition those things create. Environment may refer to the weather and ecosystem in which some animal lives, or, perhaps, the temperature…
Read the full article here