atmosphere: The envelope of gases surrounding Earth, another planet or a moon.
chemical: A substance formed from two or more atoms that unite (bond) in a fixed proportion and structure. For example, water is a chemical made when two hydrogen atoms bond to one oxygen atom. Its chemical formula is H2O. Chemical also can be an adjective to describe properties of materials that are the result of various reactions between different compounds.
cloud: A plume of molecules or particles, such as water droplets, that move under the action of an outside force, such as wind, radiation or water currents. (in atmospheric science) A mass of airborne water droplets and ice crystals that travel as a plume, usually high in Earth’s atmosphere. Its movement is driven by winds.
data: Facts and/or statistics collected together for analysis but not necessarily organized in a way that gives them meaning. For digital information (the type stored by computers), those data typically are numbers stored in a binary code, portrayed as strings of zeros and ones.
density: The measure of how condensed some object is, found by dividing its mass by its volume.
electricity: A flow of charge, usually from the movement of negatively charged particles, called electrons.
element: A building block of some larger structure. (in chemistry) Each of more than one hundred substances for which the smallest unit of each is a single atom. Examples include hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, lithium and uranium.
hue: A color or shade of some color.
iron: A metallic element that is common within minerals in Earth’s crust and in its hot core. This metal also is found in cosmic dust and in many meteorites.
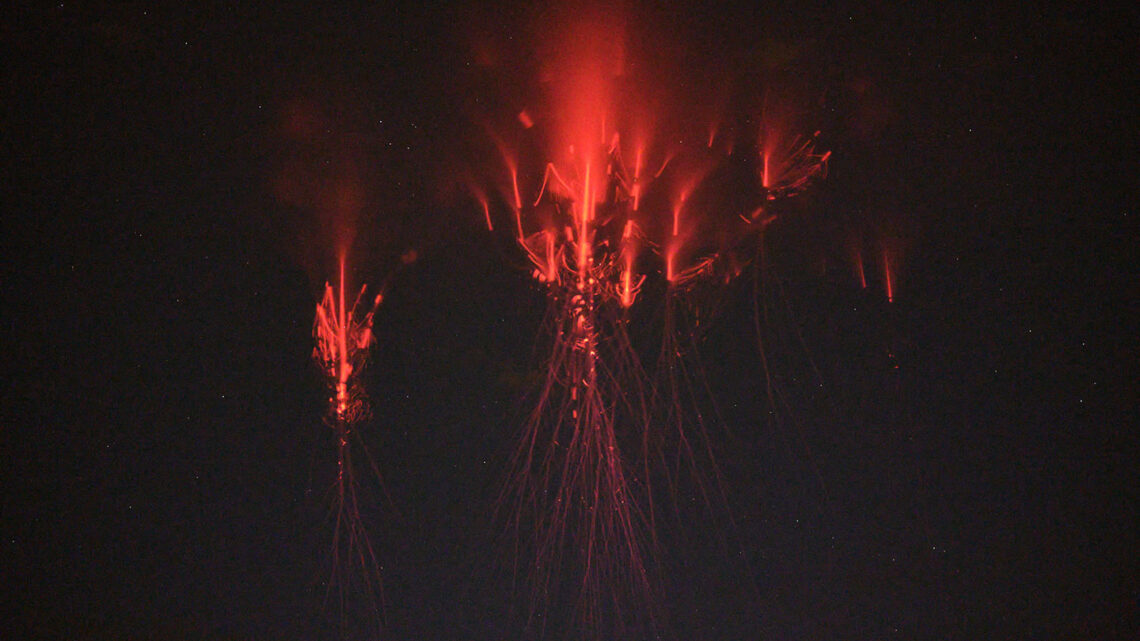
lightning: A flash of light triggered by the discharge of electricity that occurs between clouds or between a cloud and something on Earth’s surface. The electrical current can cause a flash heating of the air, which can create a sharp crack of thunder.
metal: Something that…
Read the full article here