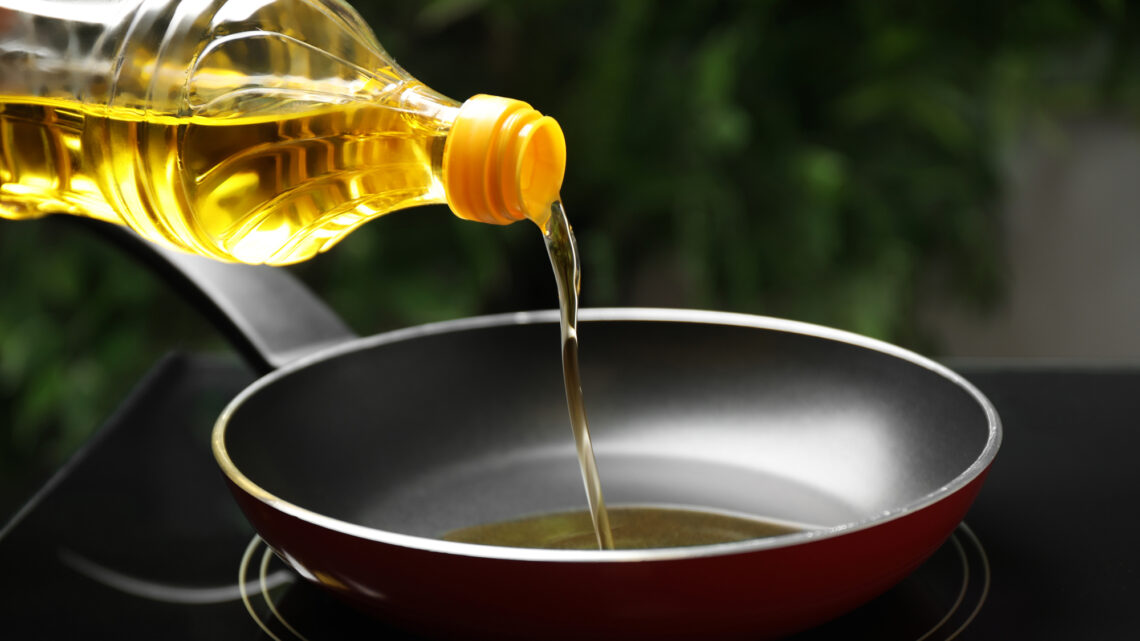
If you consume social media, you may have heard: Seed oils are terrible for your health–even toxic! Cooking oils derived from seeds cause everything from heart disease to inflammation to fatigue to bad skin–according to a certain subset of Internet influencers. Yet contrary to the posts demonizing the common ingredients, a bevy of scientific research disagrees. Here’s how to understand the health “scare.”
What are seed oils?
There’re many different types of plant-based cooking oils, but when people talk about seed oils, they’re often referencing a list of eight: Canola, corn, cottonseed, soybean, sunflower, safflower, grapeseed, and rice bran oils. (Note that things like olive, avocado, and coconut oil are absent from this list.) All of these eight oils contain fat and therefore fatty acids (an essential major nutrient group). And many (though not all) of these seed oils contain a relatively high proportion of omega-6 fatty acids.
A quick chemistry aside: fatty acids are the building blocks of triglycerides, or complete fat molecules. They are organic compounds made up of predominantly carbon and hydrogen chains with an acid group on the end. In saturated fats, every carbon except for the terminal ones have two hydrogens bonded to it. In unsaturated fats, some of those hydrogens are replaced with double bonds between adjacent carbons instead. Omega-6 fatty acids are unsaturated, and the first of those double bonds occurs at the 6th carbon from the end–hence the name.
There are multiple kinds of omega-6 compounds, but one particular type, called linoleic acid, is at the center of most of the scorn against seed soils. Linoleic acid is, again, an essential nutrient that our bodies need. We cannot synthesize it, and we need it to support healthy cell signaling, function, and immune systems.
But seed oil detractors argue that we are ingesting far too much linoleic acid, leading to the accumulation of byproducts like arachidonic acid,…
Read the full article here