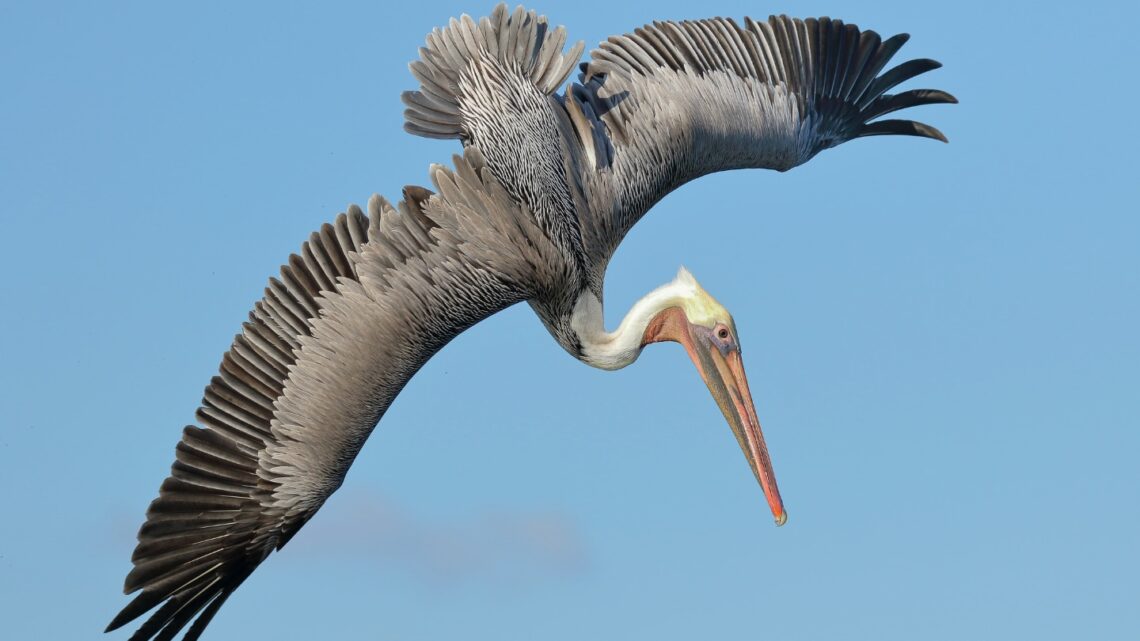
airfoil: (in aeronautics) The surface of a wing, aileron or other structure that has been designed to help lift or control an aircraft by making use of natural air currents.
angle: The space (usually measured in degrees) between two intersecting lines or surfaces at or close to the point where they meet.
birds: Warm-blooded animals with wings that first showed up during the time of the dinosaurs. Birds are jacketed in feathers and produce young from the eggs they deposit in some sort of nest. Most birds fly, but throughout history there have been the occasional species that don’t.
colleague: Someone who works with another; a co-worker or team member.
component: Something that is part of something else (such as pieces that go on an electronic circuit board or ingredients that go into a cookie recipe).
drag: A slowing force exerted by air or other fluid surrounding a moving object. It involves friction. But unlike simple friction, it increases with an object’s speed.
engineer: A person who uses science and math to solve problems. As a verb, to engineer means to design a device, material or process that will solve some problem or unmet need.
flaps: These devices are attached to the back edge of an aircraft’s wing. They increase the lift force on a wing in addition to a frictional drag force (which can be especially useful at low speeds, such as in landing).
force: Some outside influence that can change the motion of an object, hold objects close to one another, or produce motion or stress in a stationary object.
lift: An upward force on an object. It may occur when an object (such as a balloon) is filled with a gas that weighs less than air; it can also result when a low-pressure area occurs above an object (such as an airplane wing).
maneuver: To put something in a desired or necessary position by using one or more skilled movements or procedures.
model: A simulation of a real-world event (usually using a computer) that…
Read the full article here