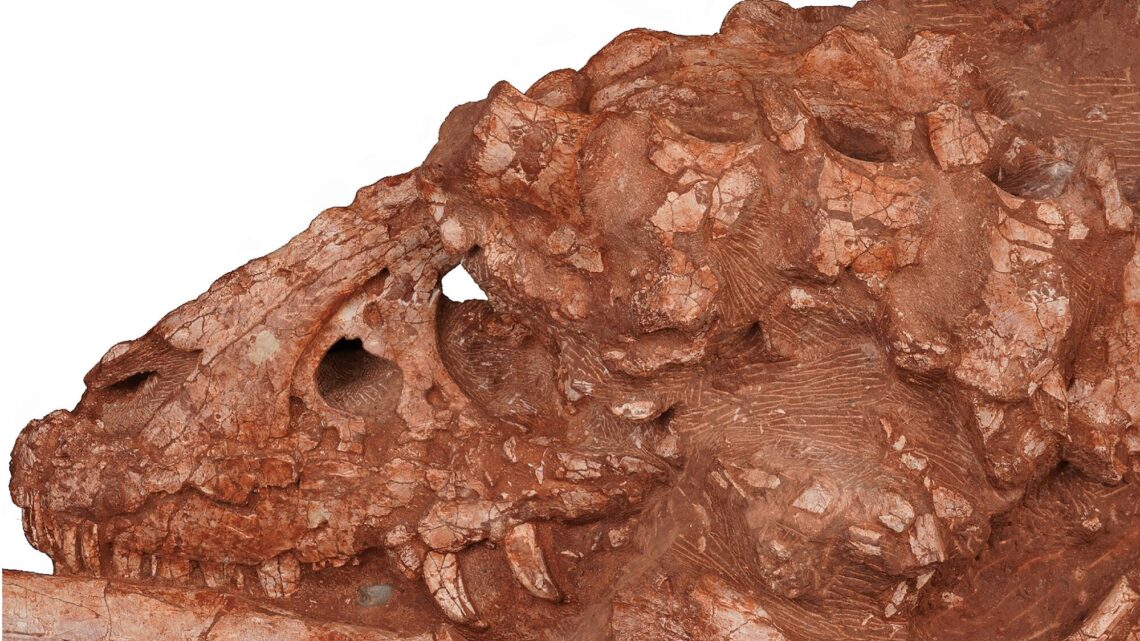
As one of the most iconic dinosaurs to ever roam the planet, the Tyrannosaurus rex gets more than its fair share of attention—so much fanfare, in fact, that many people still may not know T. rex had many evolutionary siblings. After first arriving roughly 165 million years ago, the Tyrannosauridae subfamily eventually grew to include at least 30 tyrannosaurid species. And according to a team of paleontologists, there’s at least one more species to add to the list: a “deep-snouted” tyrannosaurid they are calling Asiatyrannus xui.
Detailed in a new study published July 25 in the journal Scientific Reports, researchers at China’s Zhejiang Museum of Natural History believe fossil remains recovered in 2017 at a construction site in Ganzhou City belong to this new, smaller A. xui species. Dating indicates the dinosaur lived somewhere between 66 and 72 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous epoch, and can be considered a “small to-medium-sized” tyrannosaurine. After examining the tail, hind legs, partial vertebrae, and 47.5 cm (18.7 in) skull, experts believe A. xui grew as long as 13-feet from nose-to-tail—about half the size of its regional relative, Qianzhousaurus.
Further review indicates that compared to Qianzhousaurus, A. xui featured a “proportionally deeper snout, longer premaxilla, deeper maxilla, and deeper dentary” while lacking a “discrete horn” development. Paleontologists do note, however, that their specimen does not appear to be a fully grown adult, although it likely already passed through most growth stages. Examiners also believe these physical differences are what helped ensure A. xui’s survival in the region for millions of years. Because of its size and features, A. xui likely preyed on smaller, faster animals than its larger tyrannosaur family members.
“In southeastern China, the Qianzhousaurus undoubtedly occupied the apex…
Read the full article here