alien: A non-native organism. (in astronomy) Life on or from a distant world.
brain waves: Electrical signals produced through the coordinated activity of billions of nerve cells in the brain of an animal. When charted, the signal typically looks wavy or spiky.
cell: (in biology) The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Typically too small to see with the unaided eye, it consists of a watery fluid surrounded by a membrane or wall. Depending on their size, animals are made of anywhere from thousands to trillions of cells. Most organisms, such as yeasts, molds, bacteria and some algae, are composed of only one cell. cephalopods: Ocean-dwelling animals that include squid and octopuses.
eel: A fish with a snake-like body and no scales. Many migrate from freshwater to salt water when it’s time to spawn. Note: Electric eels are not true eels but a type of knifefish.
navigate: To find one’s way through a landscape using visual cues, sensory information (like scents), magnetic information (like an internal compass) or other techniques.
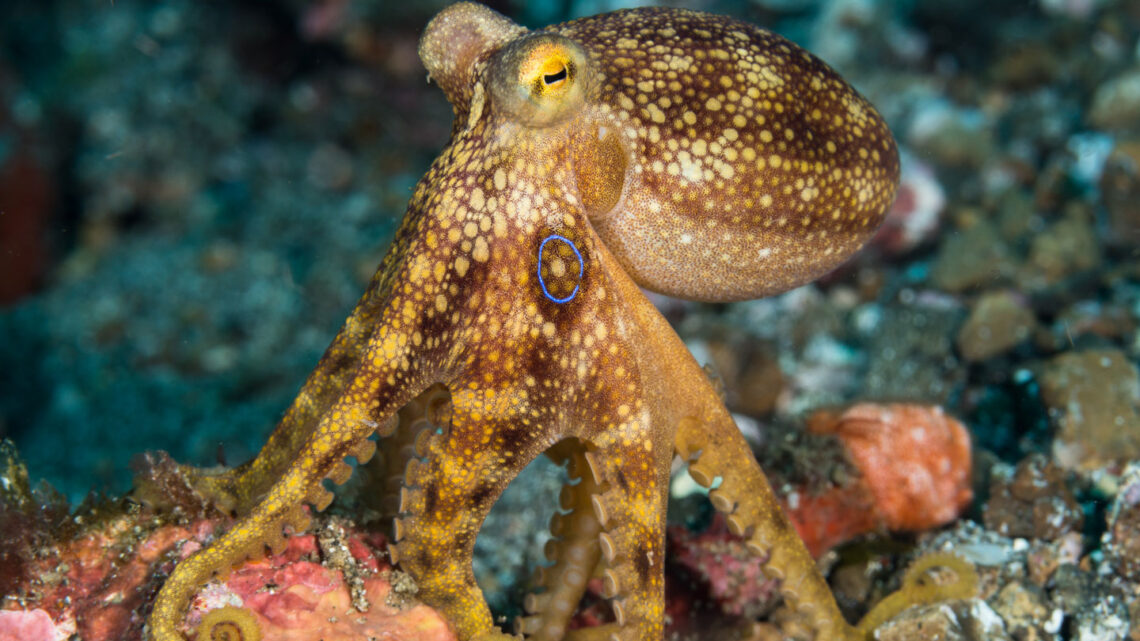
octopus: (pl. octopi or octopuses) Sea mollusks with a soft, sac-shaped body and eight arms. Two rows of suckers along each arm give the animal an ability to grasp and hold onto things. Cousins of the squids, these animals have a sharp beak-like mouth and good vision.
plume: (in environmental sciences) The movement of some gas or liquid, under the direction of gravity, winds or currents. It may be in air, soil or water. It gets its name from the fact that it tends to be long and relatively thin, shaped like a large feather.
predator: (adjective: predatory) A creature that preys on other animals for most or all of its food.
sentient: (n. sentience) An adjective to describe the ability to perceive or feel things, such as pain, boredom, awe or sadness.
shark: A type of predatory fish that has survived in one form or another for hundreds of millions of years. Cartilage, not bone, gives its…
Read the full article here