For four years now, either as a physical virus or as a looming threat, the COVID-causing pathogen SARS-CoV-2 has been the elephant in every room—sometimes confronted and sometimes ignored but always present. While once we dreamed of eradicating COVID, now much of society has resigned itself to SARS-CoV-2’s constant presence—a surrender that would once have been unthinkable.
Worldwide, there were more than 11,000 reported deaths from COVID between mid-December 2023 and mid-January 2024, and more than half of those deaths occurred in the U.S. In that same time frame, nearly one million cases were reported to the World Health Organization globally (although reduced testing and reporting means this is likely a vast undercount). In particular, epidemiologists are monitoring the newest variant of SARS-CoV-2, JN.1, and looking for any signs that it may be more severe than previous strains.
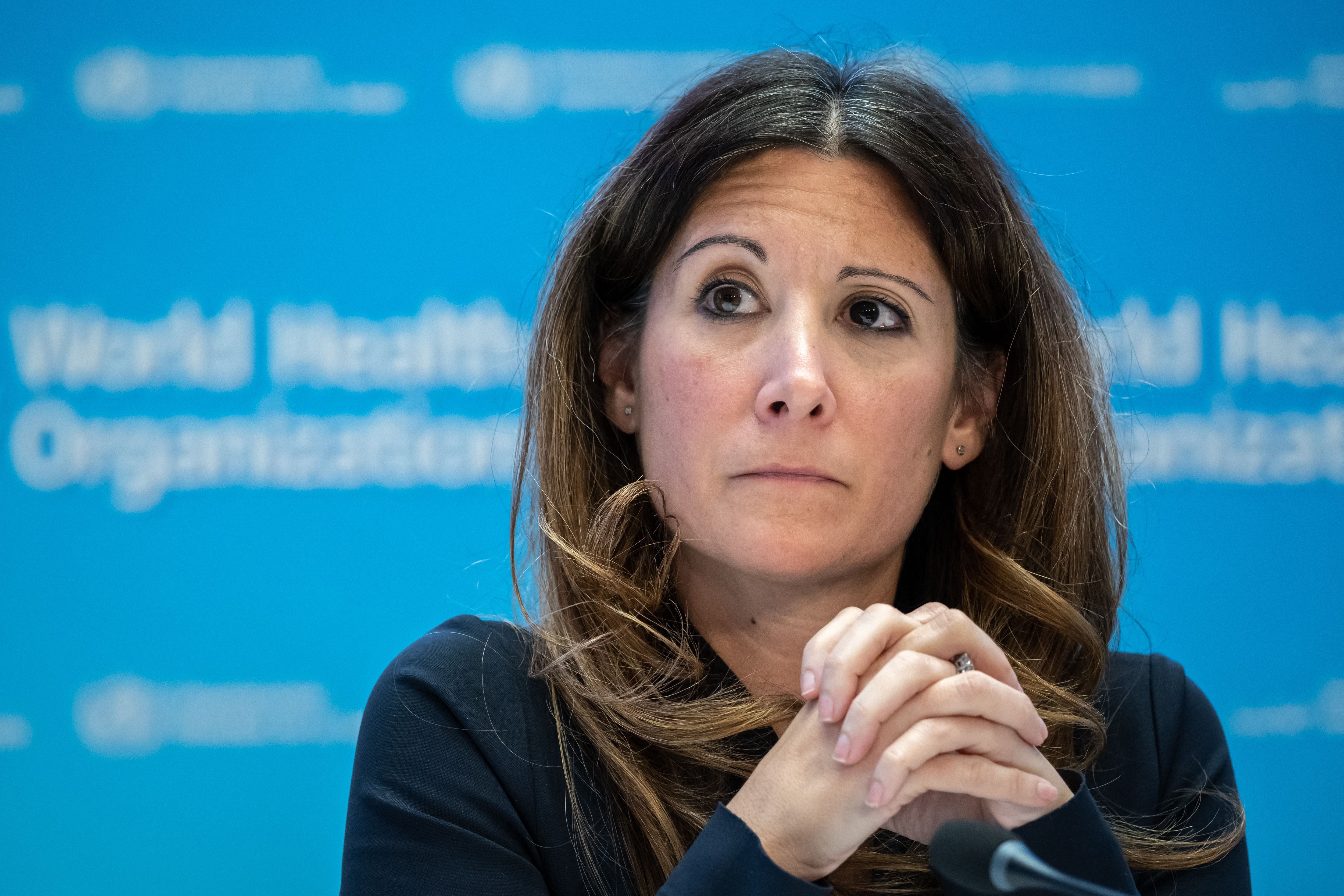
Although the WHO declared an end to the COVID public health emergency in May 2023, the organization has emphasized that the pandemic isn’t over—it’s just entered an endemic phase, which means that the virus will continue to circulate indefinitely. Throughout the past four years, Maria Van Kerkhove, now interim director of the WHO’s Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Preparedness and Prevention, has helped lead the agency’s response to COVID. Scientific American spoke with Van Kerkhove about entering the fifth year of a pandemic that many want to ignore despite its permanent impact on lives around the world.
On supporting science journalism
If you’re enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
[An edited transcript of the interview follows.]
How would you describe the overall state of COVID at this point in the pandemic?
COVID’s not in the news every day, but it’s still a global health…
Read the full article here