Arctic: A region that falls within the Arctic Circle. The edge of that circle is defined as the northernmost point at which the sun is visible on the northern winter solstice and the southernmost point at which the midnight sun can be seen on the northern summer solstice. The high Arctic is that most northerly third of this region. It’s a region dominated by snow cover much of the year.
atmosphere: The envelope of gases surrounding Earth, another planet or a moon.
climate: The weather conditions that typically exist in one area, in general, or over a long period.
climate change: Long-term, significant change in the climate of Earth. It can happen naturally or in response to human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests.
epoch: (in geology) A span of time in the geologic past that was shorter than a period (which is itself, part of some era ) and marked when some dramatic changes occurred.
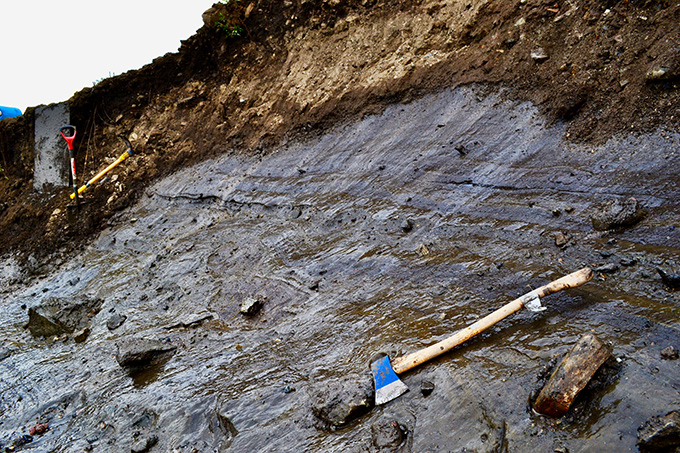
fossil: Any preserved remains or traces of ancient life. There are many different types of fossils: The bones and other body parts of dinosaurs are called “body fossils.” Things like footprints are called “trace fossils.” Even specimens of dinosaur poop are fossils. The process of forming fossils is called fossilization.
glacier: A slow-moving river of ice hundreds or thousands of meters deep. Glaciers are found in mountain valleys and also form parts of ice sheets.
ice age: Earth has experienced at least five major ice ages, which are prolonged periods of unusually cold weather experienced by much of the planet. During that time, which can last hundreds to thousands of years, glaciers and ice sheets expand in size and depth. The most recent ice age peaked 21,500 years ago, but continued until about 13,000 years ago.
interglacial: An adjective that responds to a period of relatively mild climate that exists between two successive ice ages. Earth is now in an interglacial period, one that began roughly…
Read the full article here