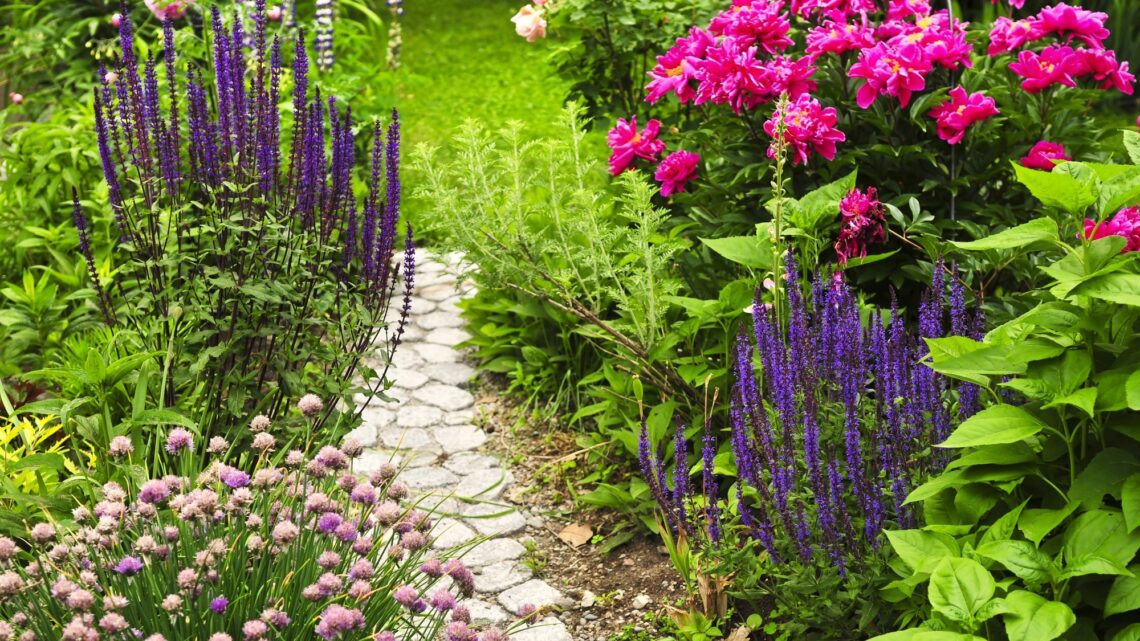
When shopping for plants, you might notice labels that specify “Zones 3-7” or similar numbers. These references indicate the plant hardiness zones where specific greenery will thrive.
Understanding your gardening zone is key to selecting plants that are suited to your region’s climate, ensuring that your garden flourishes year-round. By knowing your zone, you can make informed decisions that promote the health and longevity of your outdoor plants.
What is a gardening zone?
A gardening zone, also known as a plant hardiness zone, is a geographically defined area that helps gardeners determine which plants are most likely to flourish in the region’s climate. The USDA categorizes these zones based on the average minimum temperatures of the area. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into 13 zones based on the average annual minimum winter temperature.
In 2023, the USDA released an updated hardiness zone map in response to the impact of climate change. The updated map indicated a northward shift in the zones, reflecting the changing conditions.
Why do gardening zones matter?
Gardening zones provide essential information about your area’s climate, particularly its coldest temperatures. By selecting plants suited to your zone, you minimize the risk of winter damage, ensuring better survival rates and reducing replacement costs.
Knowing your zone also helps in planning your planting schedule, including optimal times for sowing and transplanting. Many gardening resources and nurseries offer tailored advice and products based on these zones, making it easier to find the right guidance and supplies.
What does heat zone mean?
Some plant labels also mention a heat zone. A heat zone refers to a geographic area defined by the American Horticultural Society (AHS) based on the average number of days per year that a region experiences temperatures over 86°F (30°C). These zones are specifically designed to be…
Read the full article here